Diabetic Eye Exam
Diabetes can cause numerous eye health problems that may lead to permanent vision loss if it goes untreated. If you need help managing your diabetes symptoms, visit University Retina at one of their locations in Oak Forest, Bedford Park, Lemont, and Downers Grove, Illinois. Their skilled team of ophthalmologists offers a wide range of services to help patients with diabetes prevent vision loss and maintain long-term eye health. Book a consultation online to get started, or call the office today.
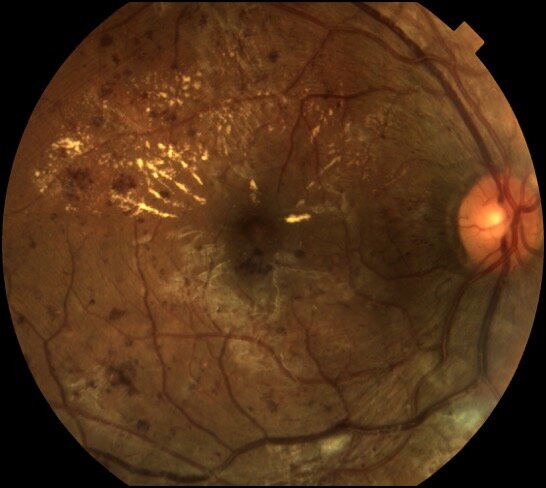
Image of Diabetic Eye Disease
Q & A
What is diabetic eye disease?
A large group of conditions can affect eye health in patients with diabetes. Among the most common are macular edema, cataracts, diabetic retinopathy, and glaucoma. Diabetic eye disease can also occur in people with prediabetes.
All diabetes-related eye conditions have the potential to cause permanent vision loss and other long-term eye health problems. But with early detection and treatment, you may be able to reverse or halt diabetic eye disease and preserve eye health.
What is diabetic retinopathy?
People with diabetic retinopathy sustain damage to the blood vessels in their retinas, which can lead to vision problems and, eventually, blindness.
What are the most common symptoms of diabetic eye disease?
The symptoms of diabetic eye disease vary, depending on the condition and how far it has progressed. But common symptoms include:
Eye fatigue
Seeing spots or floaters
Irritation and inflammation
Blurry vision, either direct or peripheral
Inability to distinguish colors
Blank or empty patches in your field of vision
Partial or complete vision loss
Since diabetes and diabetic eye disease are associated with blood sugar fluctuations and immune-system health, your symptoms might vary depending on the state of your blood sugar.
What causes diabetic eye disease?
Consistently high blood sugar levels usually cause diabetic eye disease. High glucose levels can disrupt the delicate fluid levels and damage blood vessels in your eyes. When blood vessels are damaged, they can leak fluid, which causes high pressure or scarring in the eye.
How is diabetic eye disease treated?
Your physician can treat diabetic eye disease in any of several ways. Each patient’s treatment plan is unique but may include medication to stop blood vessel irritation in the eyes, or to help lower glucose levels. Surgery is sometimes required to repair a damaged retina or other parts of the eye.
One of the most important parts of treating diabetic eye disease is helping patients manage their blood sugar levels. Your physician may recommend lifestyle or dietary changes to help keep your blood sugar balanced and prevent future eye problems.
To schedule a consultation about diabetic eye disease with a specialist, reach out to University Retina today. To get started, call the office or make an appointment online.